Batch
Batch APIs run distributed and fault-tolerant batch processing jobs on demand.
Batch APIs are a good fit for users who want to break up their workloads and distribute them across a dedicated pool of workers (for example, running inference on a set of images).
Key features
distribute a batch job across multiple workers
scale to 0 (when there are no batch jobs)
trigger
/on-job-completehook once all batches have been processedattempt all batches at least once
reroute failed batches to a dead letter queue
automatically recover from failures and spot instance termination
How it works
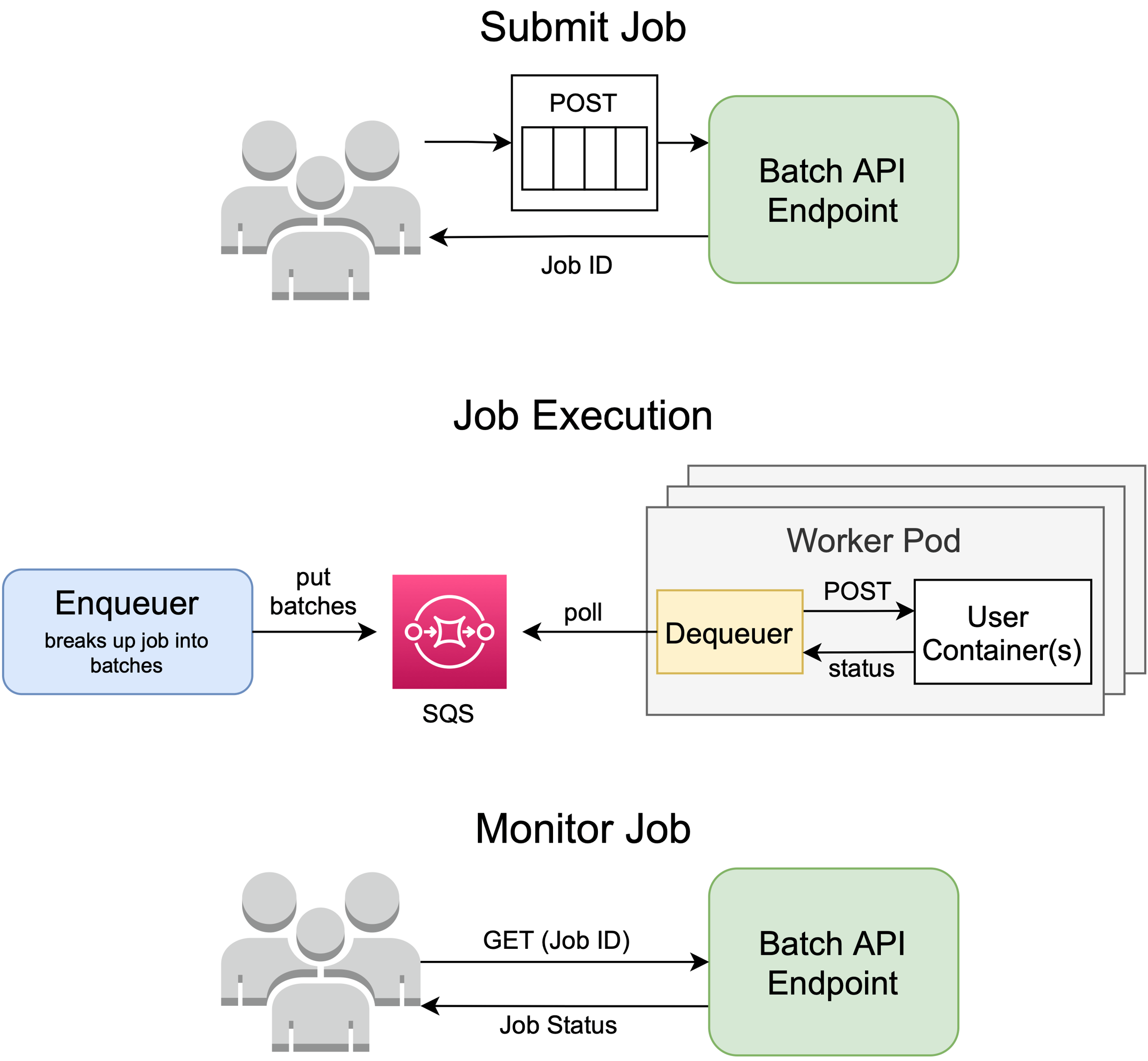
When you deploy a Batch API, Cortex creates an endpoint to receive job submissions. Upon submitting a job, Cortex will respond with a Job ID, and will asynchronously trigger a Batch Job.
A Batch Job begins with the deployment of an enqueuer process which breaks up the data in the job into batches and pushes them onto an SQS FIFO queue.
After enqueuing is complete, Cortex initializes the requested number of worker pods and attaches a dequeuer sidecar to each pod. The dequeuer is responsible for retrieving batches from the queue and making an http request to your pod for each batch.
After the worker pods have emptied the queue, the job is marked as complete, and Cortex will terminate the worker pods and delete the SQS queue.
You can make GET requests to the BatchAPI endpoint to get the status of the Job and metrics such as the number of batches completed and failed.
Last updated