Overview
Cluster
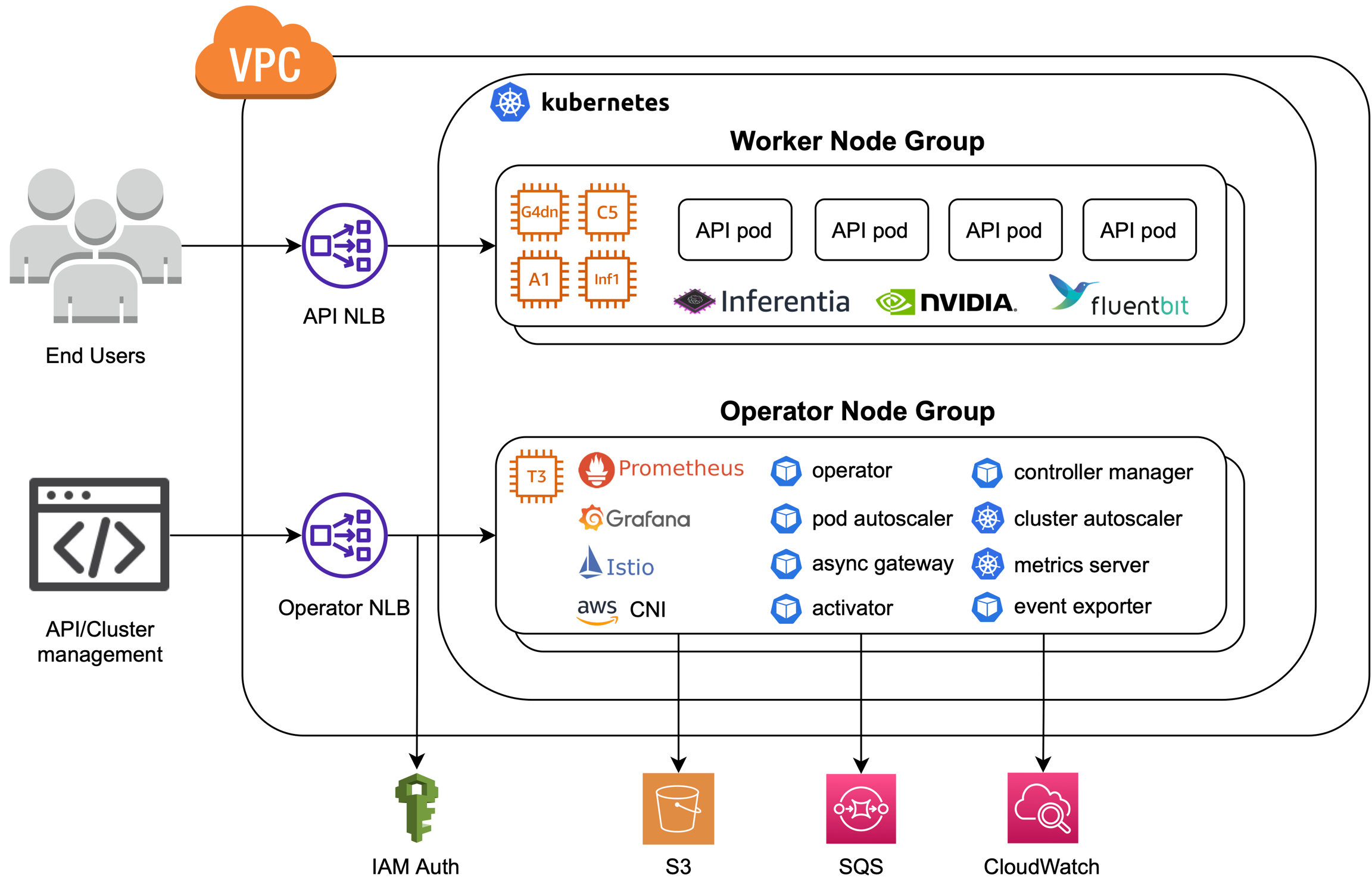
The Cortex cluster runs on an EKS (Kubernetes) cluster in a dedicated VPC on your AWS account.
Worker node groups
The Kubernetes cluster uses EC2 autoscaling groups for its worker node groups. Cortex supports most EC2 instance types, and the necessary device drivers are installed to expose GPU and Inferentia hardware to your workloads. Reserved and spot instances can be used to reduce costs.
Cortex uses the Kubernetes Cluster Autoscaler to scale the appropriate node groups to satisfy the compute demands of your workloads.
Networking
By default, a new dedicated VPC is created for the cluster during installation.
Two AWS load balancers are created to route traffic to the cluster. One load balancer is dedicated for traffic to your APIs, and the other load balancer is dedicated for API management requests to Cortex from your CLI or Python client. Traffic to the load balancers can be secured and restricted based on your cluster configuration.
Observability
All logs from the Cortex cluster are pushed to a CloudWatch log group using FluentBit. An in-cluster Prometheus installation is used to collect metrics for observability and autoscaling purposes. Metrics and dashboards pertaining to your workloads and instance usage can be viewed and modified via Grafana.
Deploying to the cluster
After a successful cluster creation, you can use the CLI or Python Client to deploy different types of workloads. The clients use AWS credentials to authenticate to the cluster.
Cortex uses a collection of containers, referred to as a pod, as the atomic unit; scaling and replication occurs at the pod level. The orchestration and scaling of pods is unique to the different types of workloads:
Realtime
Async
Batch
Task
Visit the workload-specific documentation for more details.
Architecture Diagram
Last updated