Metrics
Cortex includes Prometheus for metrics collection and Grafana for visualization. You can monitor your APIs with the default Grafana dashboards, or create custom metrics and dashboards.
Accessing the dashboard
The dashboard URL is displayed once you run a cortex get <api_name> command.
Alternatively, you can access it on http://<operator_url>/dashboard. Run the following command to get the operator URL:
cortex env listIf your operator load balancer is configured to be internal, there are a few options for accessing the dashboard:
Access the dashboard from a machine that has VPC Peering configured to your cluster's VPC, or which is inside of your
cluster's VPC.
Run
kubectl port-forward -n default grafana-0 3000:3000to forward Grafana's port to your local machine, and accessthe dashboard on http://localhost:3000 (see instructions for setting up
kubectlhere).Set up VPN access to your cluster's
VPC (docs).
Default credentials
The dashboard is protected with username / password authentication, which by default are:
Username: admin
Password: admin
You will be prompted to change the admin user password in the first time you log in.
Grafana allows managing the access of several users and managing teams. For more information on this topic check the grafana documentation.
Selecting an API
You can select one or more APIs to visualize in the top left corner of the dashboard.
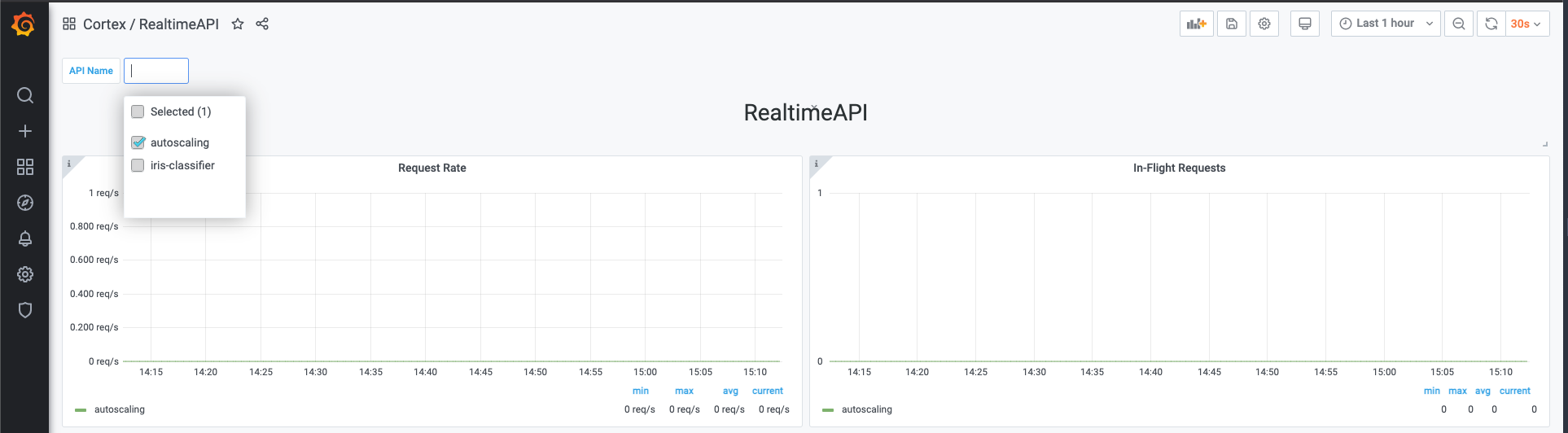
Selecting a time range
Grafana allows you to select a time range on which the metrics will be visualized. You can do so in the top right corner of the dashboard.
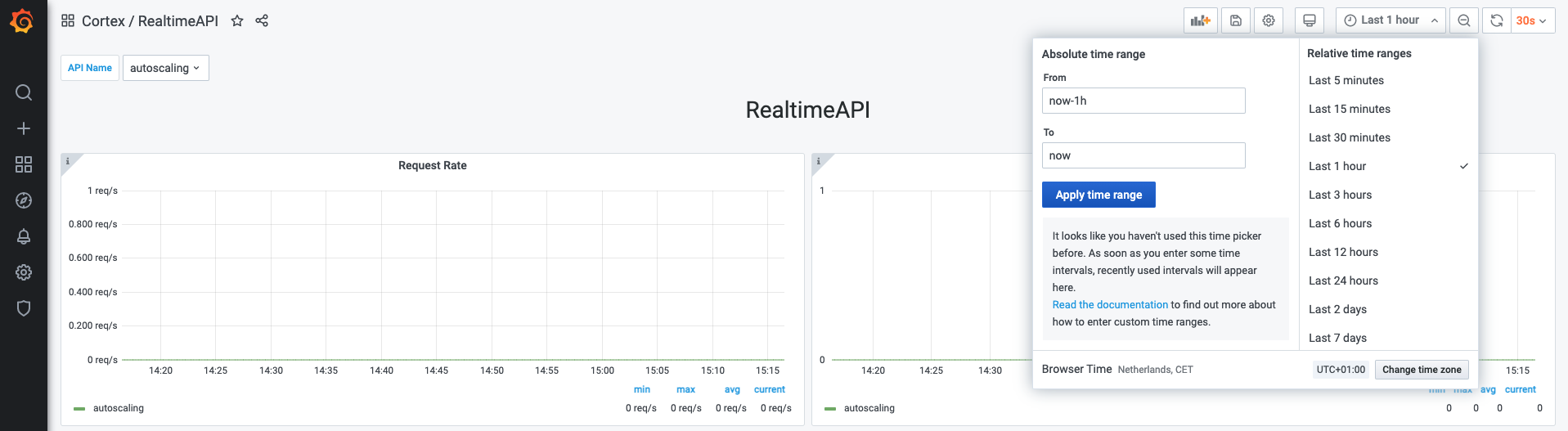
Note: Cortex only retains a maximum of 2 weeks worth of data at any moment in time
Available dashboards
There are more than one dashboard available by default. You can view the available dashboards by accessing the Grafana menu: Dashboards -> Manage -> Cortex folder.
The dashboards that Cortex ships with are the following:
RealtimeAPI
BatchAPI
Cluster resources
Node resources
Available metrics
Cortex exposes additional metrics with Prometheus. To view all available metrics, navigate to the Explore menu in Grafana and click the Metrics button.
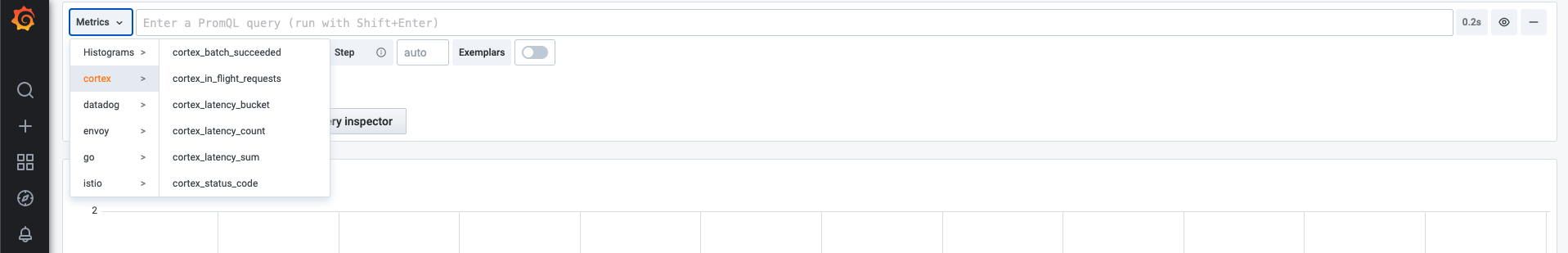
You can use any of these metrics to set up your own dashboards.
Exporting metrics to monitoring solutions
You can scrape metrics from the in-cluster Prometheus server via the /federate endpoint and push them to monitoring solutions such as Datadog.
The steps for exporting metrics from Prometheus will vary based on your monitoring solution. Here are a few high-level steps to get you started. We will be using Datadog as an example; feel free to reach out to us on Slack if you need help setting up your monitoring tool.
Configure kubectl
Follow these instructions to set up kubectl.
Install agent
Monitoring solutions provide Kubernetes agents that are capable of scraping Prometheus metrics. Follow the appropriate instructions to install the agent onto your cluster (here are the instructions for Datadog).
Scrape Prometheus
Some agents require a Prometheus endpoint to scrape directly. You can provide http://prometheus.default:9090/federate?match[]={job=~".+"} as the target url to indicate that all metrics should be scraped.
Some agents look for targets to scrape via annotations. You can update Cortex's Prometheus server with the correct annotations. First, Create a patch.yaml file and add the relevant annotations for your monitoring solution. Below is an example for Datadog. These annotations instruct the Datadog agent to scrape the Prometheus server at the endpoint /federate?match[]={job=~".+"} and extract cortex_in_flight_requests. Note that Datadog specifically requires the query params in the Prometheus url to be encoded.
Then, update Prometheus with your annotations:
Long term metric storage
Prometheus can be configured to write metrics to other monitoring solutions or databases for long term storage. You can attach a remote storage adapter to Prometheus that will receive samples from Prometheus and write to your destination. You can find a list of Prometheus remote storage adapters here. Additional remote storage adapters can be found online if yours isn't on the list.
Once you've found an adapter that works for you, follow the steps below:
Configure kubectl
Follow these instructions to set up kubectl.
Update Prometheus
Define a patch.yaml file with your changes to the Prometheus server:
Update Prometheus with your changes:
Last updated